1] Life of Karl Marx
Karl Marx was a German philosopher, economist, historian, and revolutionary socialist, best known for his critique of capitalism and his influential role in developing modern communism. He was born in 1818, in Trier, Prussia (now Germany), into a middle-class family. His father was a lawyer who converted from Judaism to Protestantism, largely for career reasons.
Marx studied law and philosophy at the universities of Bonn and Berlin, where he was influenced by German idealist thinkers, especially Hegel. In the 1840s, he moved into journalism and became editor of a radical newspaper, Rheinische Zeitung, (Rhenish/Rhineland Newspaper) which was soon suppressed by the Prussian authorities due to its political content.
Forced into exile, Marx spent much of his adult life in France, Belgium and eventually England, where he lived in poverty for decades. It was during his time in Paris that he met Friedrich Engels, his lifelong friend and collaborator. Together, they wrote The Communist Manifesto (1848), which called for the working class to overthrow capitalist societies.
Marx’s major work, Das Kapital, was published in 1867. It analysed the capitalist mode of production and argued that capitalism was inherently exploitative and would eventually be replaced by a classless, communist society.
He remained politically active throughout his life, supporting labour movements and revolutionary causes. Karl Marx died in1883, in London. Though largely ignored during his lifetime, his ideas profoundly shaped 20th-century political thought and movements.
2] Introduction to Marx
“Philosophers have only interpreted the world, what matters is to change it.” – Karl Marx
Marx is certainly the greatest of all political philosophers. No other philosopher has such an influence like that of Karl Marx. Marx himself has written that “Philosophers have only interpreted the world, what matters is to change it.”
Marx calls his theory as Praxis. Praxis means action based on theory and theory leading to action. It means whatever we do should be based on the proper understanding and on the basis of understanding we should formulate our policies.
Marx was concerned with the extreme exploitation of the poor, by the capitalist class. Hence, he wanted to end the exploitation and to give a life of dignity to the poor. He was critic of capitalism. He considered capitalism as inhumane.
Since Marx is a critic of capitalism, he is a believer in socialism. Thus Marx is a socialist.
Difference in capitalism and socialism?
Capitalism denotes private ownership over the means of production. In capitalism the motive of production is profit rather than need.
Socialism is a modern philosophy. It emerged as a reaction against capitalism. It is based on the realization of inhumane nature of capitalism. According to the socialists, industrial society can be based on socialistic principles. It is not necessary to base it on capitalist principles.
How Marx defines his Socialism?
He calls his socialism as scientific. He calls his socialism scientific and socialism before his socialism as utopian.
Marx was not the first person to give the socialist ideas. Socialist ideas emerged in French revolution (the ideas of equality and fraternity). During French revolution, there were socialist / left revolutionaries. Like Louis Blanc.
Later on there were socialist ideas in other countries of Europe e.g. In Britain Robert Owen, who is also known as ‘father of cooperative movements’. French revolutionaries proposed violent method and British socialist proposed peaceful method. They proposed appealing to the conscience of the capitalist. Marx called them as utopians because Marx believed that socialism cannot come by their methods.
The revolutionaries were ready for action but lacked the understanding. Similarly those who were trying to bring socialism through peaceful means, lacked both – the understanding as well as action. Hence Marx suggests that they were utopians, Marxism is a science, Marxism is a praxis.
Marx does not believe in the concept of conscience. He does not believe in God or idea. Hence there is no point appealing to God or conscience. Hence Marx suggests – “workers of the world unite; you have nothing to lose except your chains.” Chains denote religion, nation etc.
Aim of Marx’s socialism, to establish communism.
What is Communism?
Communism is utopia of Marx; it is Marx’s ideal state – Marx’s ideal state and Gandhi’s ideal state both are stateless societies. Both Gandhi and Marx are anarchists. Anarchy in literal sense means absence of state. There are two ways in which scholars have described anarchy.
1] Hobbesian View: Anarchy is a painful situation. Life of man will be in chaos. Man cannot live in peace with others, in the absence of the state.
2] Marxist view: Anarchy is the state of perfect happiness, perfect freedom. State is an instrument of exploitation. Man is social by nature; man has enough reason to live in peace with others. How life will be governed in the absence of state? The role of state will be taken up by voluntary associations or self-help groups.
Communism is a classless society. It is because private ownership is abolished, property comes under common ownership. Hence there are no class divisions, all belong to one class. Since classes will end, state will become redundant and state will wither away. There is lot of similarity between Marx’s communism and Gandhi’s Ram Rajya. The only difference is in methods.
Gandhian method gives peaceful appeal to the conscience of the capitalist class.
Marxist method suggests violent overthrow of capitalism. In the words of Karl Marx “Violence is the mid-wife of change. There has been no birth without blood.”
Prominent works of Marx
Young Marx and Mature Marx. (COMMUNIST MANIFESTO – theory of revolution
3] Influences on Marx
1] French revolution. He was influenced by the ideas of equality and fraternity.
2] British school of political economy. It is a discipline where economic policies of the state are analysed. Adam Smith is considered as father of political economy. His book “The wealth of Nations” is called as the first text book in political economy. Adam Smith was critic of mercantile capitalism and the exponent of industrial capitalism. Marx held that Adam Smith’s policies will not bring wealth to the nation, it will limit wealth to the small section. For addressing the poverty of all, the only way is common ownership over the means of production.
3] German philosophy and Hegel
A] Hegel
Hegel was the official philosopher of Prussia. Hegel has given very strong defence to the state. Hegel compared state with God. In the words of Hegel, “State is a march of God on earth.” God is absolute idea or universal spirit. For Hegel, idea is the ultimate reality. (Hegel is idealist like Plato), God is absolute idea, or ultimate reality, state is reflection of God on this earth.
For Marx idea is ‘false consciousness’. Idea is not real, matter is real. God has not made man; man has made God. According to Marx, idea is false consciousness, religion is opium of masses. According to Marx, Hegel is standing on his head, he has to stand on his feet to understand what is real.
“State is a march of God on earth.” – Hegel
Progress of history: God -> Physical World (Mountains, Land, Water) -> Trees -> Birds -> Animals -> Man -> Family -> Civil Society -> State.
According to Hegel, everything in this world is the reflection of God. The maximum amount of God is present in the state. State is nearest to God. Hence, we should worship the state. How do we know that God is a creator of this world? When we look at the things of this world, the question comes to our mind, who is creator? Our reason tells us that God is creator.
“The real is rational, and the rational is real” – Hegel
This famous statement by G.W.F. Hegel captures the core of his idealist philosophy.
1. “The real is rational”
In this part, Hegel is explaining what counts as truly real. Like Plato, Hegel does not believe that reality is limited to what we can touch or see. Instead, he argues that what is real must be intelligible — it must make sense when understood through reason. So, if something can be fully understood by rational thought, then it is real in the truest sense.
According to Hegel, ideas, especially the highest idea — which he calls the Absolute Idea or God — are the most real. God, for Hegel, is not a personal deity but the embodiment of reason, purpose, and total understanding. Thus, God is the highest reality, and since we can grasp this through reason, it proves that the real is rational.
2. “The rational is real”
This second part expresses Hegel’s political purpose. It means that what exists in the world — especially established institutions like the state — are not accidental or arbitrary, but have a rational basis behind them.
Hegel believed that the modern state, especially the constitutional monarchy of Prussia in his time, was not just a human creation but an embodiment of rational freedom. He described the state as “the march of God on earth”, meaning that the state represents the unfolding of divine reason in human history.
Why equate the state with God? Because, like God, the state — when properly understood — is seen as a rational structure that cares for all its members, ensures justice, and upholds order.
To sum up, “real is rational” suggests that true reality is not what we see, but what we can understand through reason — especially ideas like justice, freedom, and God. On the other hand, “rational is real” means that institutions like the state are not random; they are rational structures that reflect deeper truths, and deserve our allegiance.
4] Principles of Marxism
Marxism means the political doctrine of Marx which aims at the violent overthrow of Capitalism. Marx described his principles as scientific. Marx used to consider himself as scientist. However Marx followers projected him as God. Marx is known as a ‘God, that has failed.’
A] Concept of Dialectics
Dialectics is a concept given by Socrates. Dialectics is a method to understand the truth. Dialectics represent rational dialogue or rational debate.
It represents argument, counter argument and synthesis or conclusion. Arguments and counter arguments continue till final synthesis emerges. Dialectics can be represented through the equation. Thesis + antithesis = synthesis.
Hegel’s Contribution
Hegel has used the concept of dialectics to show ‘the nature of movement of history.’ History is a movement of idea.
There are three laws of dialectics
- Unity of opposites
- Negation of negation
- Quantity changes into quality.
1] Unity of opposites: In all the things, exists its opposition. Opposition is a force of history.
2] Negation of Negation: As per law of history, force negativity gets negated.
3] Quantity changes into quality: Changes do not happen overnight; first quantitative changes take place and it gives rise to qualitative change. It may appear new, but it is not entirely new. New has roots in the old. Once contradiction ends, movement ends, history ends.
According to Hegel, human history ends with the formation of state.
B] Historical Materialism
Historical materialism is economic interpretation of history. Its purpose is to explain history, causes of history. Marx wanted to change capitalism and establish communism. He wanted to know, how history changes, which factors play the role.
Marx first analysed Hegel’s theory of history. Hegel’s theory of history is idealistic interpretation of history. According to Hegel, history is the result of dialectical movement of idea. Marx suggested that Hegel’s theory is not a scientific explanation of history rather political/ ideological/ teleological explanation of history. Marx claims his theory as scientific.
In order to understand history scientifically, we have to understand what was the first historical act of man. He wanted to know whether thinking or action is more important. According to Marx,
“In order to make history, man has to live. In order to live man has to eat. In order to eat, man has to work or perform action.” – Karl Marx
Implication of above statement:
Between the manual labour and the intellectual labour, more important is manual labour. Society can live without the work of intellectuals, but society cannot live without the work of manual workers. It is ‘false consciousness to think that the role of intellectuals more important than those of workers.
He blames thinkers like Plato and Aristotle, who established that those who are men of reason are ought to be master and permanently deprive those who perform manual work.
According to Marx, intellectual class is exploiter class. Worker should never listen to intellectuals, Philosophers, church father, they only generate false consciousness. For example, in Indian context, we can compare intellectuals with Brahmins, giving theories justifying the subordination of Sudras and Dalits.
C] Concept of Society
Origin of Society
According to Marx, society is the division of labour. People form the society for the task of production. Production is a necessity for survival. Production is a social activity. It cannot be done alone. Thus, the basic structure of society is the economic structure and all relations are ‘relations of production.’ Economic structure means, structure of production or the material structure. The earliest society is, the society of hunters and gatherers.
D] Base-Superstructure Model
Marx is a structuralist. He has studied the society as a structure. According to him, economic structure is the fundamental structure or basic structure.
Marx’s base and superstructure model of society:
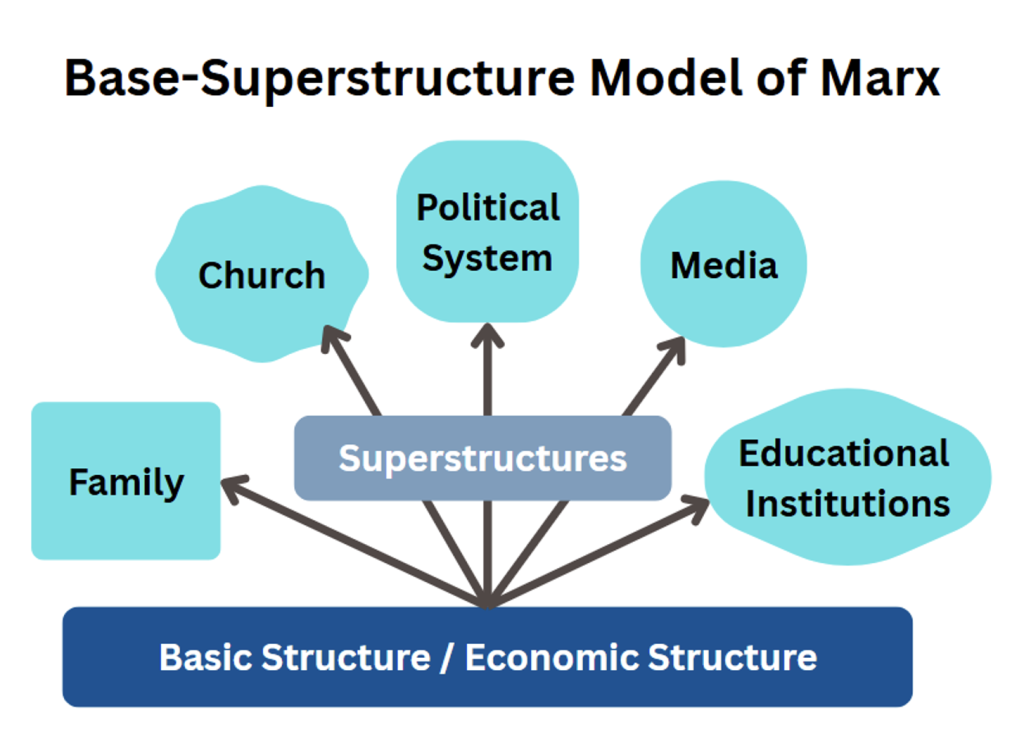
Economic structure is the basic structure. Whatever happens in the society, economy is the factor. State, church, family, educational institutions, media etc. are all superstructure.
Superstructure is a reflection of base. Superstructure is not independent of base. It is grounded in the base. The nature of base will determine the nature of superstructure. e.g. If mode of production is feudal, family system will be joint family. If mode of production is capitalist, there will be nuclear families.
Even the ideas or ideologies will be shaped by economic system. When economic system will become capitalist, the ideology of individualism will be promoted.
Hence there is no point studying the elements of superstructure. What is needed is to understand the features of basic structure. Thus there is no point changing the political system without changing the economic system.
E] Relations of Production
When man enters into system of production, either he enters as owner of means of production (haves) or non-owners. (have-nots). Haves will have bargaining power over have-nots. One will be the exploiter and the other will be exploited. Man’s relations with the mode of production explain his class. There are two classes in the society. Haves and Have-nots. What type of relationship can be there between haves and have-nots? It will be a relationship of exploiter and exploited. Hence it will be a relationship of struggle or class struggle. Hence there will always be, a conflict of interest. The real identity of a person is identity of his class and not of his religion or nation. Hence, the real politics is the politics of class. What is the message? Worker should understand that their real interest is with the members of their class. They should not develop the false consciousness that the other person belongs to his nation or religion. Hence the workers of the world have to come together, they have common interest. (Proletarian internationalist). Thus for Marx, poor Hindu and poor Muslim have common interest rather than poor Muslim and rich Muslim.
F] Marx on Revolution
Revolution means total change. Revolution means when the mode of production changes. Political revolution is no revolution.
From Marxist point of view, there is nothing called revolution in India. It was just a transfer of power from British to India. In India, the basic structure remained intact. It remained feudal. Hence there is no change in the situation of masses or rural poverty.
In China, peasant revolution took place. It was a violent overthrow of feudalism. In China, peasantry established control over land. In China communism has been established in land.
G] Marx on False Consciousness
“Religion is opium of the people.” Karl Marx
“Nation or nationalism is an ideology or a false consciousness created by the propertied class to break the solidarity of workers.” – Karl Marx
On similar lines, Marxist scholar Benedict Anderson calls nationalism as ‘Invented tradition.’
What poor should do?
They should come out of false consciousness and develop true consciousness. False consciousness emerges when we listen to the intellectuals.
To develop true consciousness, one has to stand on his feet. One should look at the material conditions of your life. Understand the objective conditions of your life objectively, rather than subjectively e.g. Gandhi used the term Harijana for Dalits. It is a subjective understanding, not the objective understanding. According to Ambedkar, Harijana is a misguiding term. They are actually the depressed classes.
Marx has explained consciousness at two levels. 1. Class in itself 2. Class for itself
Class in itself.
Class in itself denotes low level of consciousness. When person understands that he belongs to a particular class or when worker understands that he is from working class and the capitalist is from the other class.
Class for itself.
This is high level of consciousness. True consciousness. When worker understands his exploitation. When worker will understand his exploitation, he will become class for itself. He will take up the arm in his hand.
When exploitation reaches to its extreme, class in itself changes in class for itself
“It is not our consciousness that determines our existence, it is our existence that determines our consciousness.”
The above statement is from Marx’s concept of historical materialism. Marx has criticized Hegel. According to Hegel, idea is real (real is rational). According to Marx, Hegel is standing on his head.
It is matter and not idea that is reality. On the basis of the base superstructure model, Marx has shown that economic structure is the basic structure, idea, ideology, religion is a part of superstructure. Superstructure is never independent of base.
The class which controls the economic structure, also controls the superstructure. The real interest is the interest of the class. Ideology, religion, develop false consciousness. Working classes should understand their class interest, they should go for the objective understanding of their objective conditions. Once they will understand conditions of their condition, they will develop true consciousness.
The class in itself will change into the class for itself. Once the true consciousness comes, it will not be possible to exploit them anymore.
5] Criticism of Marx
A] Reductionism
Marx has been criticized as reductionist – He has reduced the complex phenomenon of history to the single cause i.e. Economic cause. Hence his theory is called as ‘economic determinism’.
His economic reductionism has not only been criticized by non-Marxist like Max Weber as well as Neo-Marxist like Althusser.
Max Weber criticized Karl Marx for monocausal explanation of history. Max Weber in his book ‘Protestant Ethics and Rise of Capitalism.’ has shown how superstructure in words of Marx like religion, has given rise to capitalism
Even before Althusser, Gramsci found flaws in Marx’s theory of History. Marx has ignored the role of cultural and ideological factors shaping history.
Althusser has given ‘Law of Overdetermination’. Means economic factor is overdetermined in Marx. Althusser has given multi structural approach. Althusser has studied Russian revolution. Russian revolution emerged from political structure and not from economic structure.
B] Marx as a Determinist
Determinism is called as non-scientific thinking. Determinism represent fundamentalism. Determinism imply that a person believes that his view is scientific, ultimate truth and cannot be questioned. Marx claimed himself to be scientific. He rejected all earlier explanations as false consciousness. For followers of Marx, ‘Marx was God’. Since Marx was projected as God, it was believed that all of his predictions are bound to happen. However time has proved that ‘Marx was a God that has failed.’
Karl Popper in his book ‘Open Society and Its Enemies’ called Plato, Hegel and Marx as enemies of open society. Karl Popper has criticized Hegel and Marx for committing the guilt of ‘Historicism’. It denotes ideological interpretation of history. Or politically motivated explanation of history.
According to Karl Popper, Marx’s theory cannot be considered as ‘scientific’. It does not fulfil the criteria of falsification : It is a criteria to regard a particular theory as scientific in social sciences. In social sciences we cannot have theories based on experiments, as happens in natural sciences. In social science, a theory can be regarded as scientific if it is open for ‘critical evaluation or examination.’ Scientific theories are possible only in open societies because of freedom of speech and expression. It cannot be produced in closed societies.
6] Dialectical Materialism (2nd Theory of Marx)
Marx has borrowed the concept of dialectics from Hegel. The only difference is that Hegel has given dialectical idealism, Marx has given dialectical materialism. According to Hegel, history is a product of dialectical movement of idea. According to Marx, history is the product of the dialectical movement of matter. According to him, economic structure is the basic structure. He has also given the three laws. (Unity of opposites, Negation of Negation, Quantity changes into quality.)
Central theme in the idea of dialectics is the concept of struggle or contradiction. It is because of the struggle, history moves.
A] Theory of Class and Class Struggle
“The history of all, hitherto existing societies is a history of class struggle.” – Karl Marx
History is because of class struggle. Means dialectics between classes or conflicts of interest between the two classes. One is ‘have’ the other is ‘have-nots’. One is exploiter, other is exploited. Relation between exploiter and exploited has to be the relation of struggle.
The theory of class struggle is based on the theory of historical materialism. Class struggle is located in the mode of production. In all class divided societies, there will be class struggle.
B] Stages of History
Marx has given the following stages of human history. History denotes change in the mode of production. Means of production, Forces of production and relations of production.
1] Prehistoric stage: Primitive Communism
Initially property was held in common. Hence no classes, no struggle, no state. Why he has given the concept of primitive communism? This is to show that man once lived without private property and without state also.
2] Slave society: Masters and Slaves
Since classes, so class struggle and so state.
3] Feudalism: Feudal and Serfs
Since classes, so class struggle, so state develops.
4] Capitalism: Two classes – Capitalist and workers
This is contemporary stage.
5] Socialism
This is a stage which will come immediately after communist revolution which will overthrow capitalism. Two classes. Workers and capitalists. Worker will be the exploiter. Now state will be controlled by the workers. Hence Marxist scholars also prefer to call this stage as dictatorship of proletariat.
6] Communism
There will be a peaceful change from socialism to communism. Classes are abolished. State will wither away. State of perfect freedom and perfect equality. Perfect happiness. Since classes will end, history will end.
C] Comparison between Capitalism and Socialism
Comparison between Capitalism and Socialism
| Capitalism | Socialism (Dictatorship of Proletariat) |
|---|---|
| Two classes: Capitalists and Workers | Two classes: Capitalists and Workers |
| Capitalist class exploits the working class | Working class overthrows and dominates the capitalist class |
| State is an instrument of the capitalist class | State is an instrument of the working class |
| Democracy of the minority (capitalist class) — dictatorship of the minority over the majority | People’s democracy — dictatorship of the majority over the minority |
| Claims to reward according to work, but in practice exploits workers | “From each according to his ability, to each according to his work” |
| Workers are forced to work beyond their ability and underpaid | Workers are recognized as the primary productive force and rewarded fairly |
D] Comparison between Socialism and Communism
Comparison between Socialism and Communism
| Socialism | Communism |
|---|---|
| Classes still exist | Classless society |
| State exists and is controlled by the working class (proletariat) | Stateless society |
| Not a perfect democracy; it is the dictatorship of the proletariat | Perfect democracy |
| “From each according to his ability, to each according to his work“ | “From each according to his ability, to each according to his need“ |
| A transitional phase after revolution | Final stage of historical development — the end of history |
| Implemented in various forms (e.g., USSR, China) | Remains a utopia; never fully realized in practice |
Socialism : In countries like Russia, China, Cuba, Vietnam, N Korea communist revolution took place but instead of socialism or dictatorship of proletariat, what emerged was the dictatorship of communist party. Workers never got power, power got centralized in the hands of the elites or the leaders of communist party. Hence instead of people’s democracy, what emerged was oligarchy of communist parties. Communist party established its totalitarianism or totalitarian regime. Hence the amount of freedom and equality which people enjoy in western countries, not a fraction of that freedom and equality was available in these societies. Hence, they were called as closed societies / tyrannies. USSR ultimately collapsed. China continued because it started economic reforms in late 70s.
7] Failure of Marx
Lenin is responsible for failure of Marx. Lenin is also a ‘Peter, who denied his master’. It is said that biggest harm to Marx was caused, not by his opponents, but by his supporters. If today Marx is considered as enemy of open society, advocate of totalitarianism, it is because of Lenin.
More than Marx’s followers, Marx’s opponents understood the message of Marx.
A] Message of Marx
Marx himself knew that communism is a utopia. He only wanted to make capitalism humane. The western world understood Marx, incorporated the concern of social and economic equality, it has given rise to the concept of welfare state.
B] Lenin
Lenin considered Marx as God. He believed that Marx’s ideas are bound to emerge. However, during the time of Lenin, there were no signs that history will move as per suggested by Marx.
Why history did not move according to Marx?
The nature of capitalism had changed. Some developments took place, Marx had ignored these developments.
Because of imperialism, the location of exploitation shifted from the western world to colonies. Capitalists could profitably invest the wealth in colonies, they have expropriated huge returns, drain of wealth. Hence, they could afford to give higher wages as well as state could provide social security i.e. Improved the situation of poor. Revolution happens when exploitation becomes extreme. However, in western countries scenario changed. Lenin was man of action; he was determined to implement communist ideas. Hence, he brought some modifications in Marxism. He has expressed these ideas in his book ‘WHAT IS TO BE DONE?‘.
C] Lenin’s Changes
Lenin made 3 changes. 1. Communist revolution in feudal country. 2. The role of communist party. 3. The role of peasantry.
1] Revolution in Feudal Country
According to Karl Marx, communism will come where capitalism is in advanced state. Why? When capitalism will reach to its advanced stage, all of its contradictions will come to the surface. What Lenin did? Lenin thought we can cut short the history. He has chosen Russia where industrialization just started.
2] Concept of Communist Party
Marx was against the idea of communist party. Marx wanted ‘spontaneous revolution’ by workers. Marx wanted that workers should be fully conscious of their exploitation; it will automatically result into emergence of revolution. He wanted that we should wait till ‘class in itself change into class for itself’. Why? Only when workers are fully conscious, no one will be able to exploit. If we bring party, there will be hierarchy, domination and equality will remain elusive.
Lenin felt that workers will not be able to develop consciousness on their own. Hence consciousness can be injected from outside. Who will inject? Communist party. Communist party will be led by ‘middle class intellectuals’. Lenin himself was from middle class. According to Lenin, Communist party will act as ‘vanguard of revolution’. (Vanguard – Friend, Philosopher, Guide). On the contrary Marx never gave any role to the intellectuals, Marx used to consider intellectuals as exploiters.
3] Role of Peasantry
According to Marx, communist revolution will come only through the proletariats. Who are proletariats? Property less class. In western countries, workers during his time were proletariats. According to him, propertied class can never be revolutionary. Workers will be revolutionary because they are also the most exploited class. Marx never considered peasantry revolutionary. They do have some amount of land and low level of consciousness. What Lenin did? In Russia, the number of workers was very small, it was primarily an agrarian society. Hence, he incorporated peasantry within the revolutionary class.
The cumulative effect of Lenin’s innovations ultimately resulted into a situation where the dictatorship of the communist party got established. Lenin was still progressive, but when Stalin came USSR became totalitarian state.
8] Contradictions of Capitalism
“Capitalists dig their own graves” – Karl Marx
It shows contradictions in capitalism which will result into the destruction of capitalism on its own.
The purpose of production should be need, whereas in capitalism it becomes greed or profit.
Capitalism creates the contradiction between man and society. The other person is not a fellow human being rather a competitor, a source of insecurity.
In capitalism, labour of the worker becomes the source of his own exploitation.
Capitalism is driven by profit. To maintain profit, we have to keep the cost of production low. To keep the cost of production low, workers will be given low wages.
A] Capitalist Law of Wages
Worker cannot be given more than what is enough for his survival, he cannot be given the surplus because he may not come back to the work next day.
Wages are already low and to maintain the profit maximum they decrease wages capitalist will bring technology, others will be also forced to do the same. It will result into loss of job of workers. It means reduction in workers bargaining power.
Worker will be more in number; hence they will be forced to work at low wages.
As capitalism will advance, its contradictory nature will become more and more clearer. The exploitation will keep on increasing.
B] Disappearance of Middle Class
Capitalism is monopolistic in nature. Competition will become more and more tough.
Only few capitalist will be able to survive. Small players in the Market will keep going/ coming out of market. They will also join the rank of workers. A situation will emerge where society will be divided into two classes. Haves and Have-nots. This situation is called polarization of classes. On one hand, small number of people will be holding the entire amount of the wealth in the society. On the other hand, there will be mass poverty. This is a situation of dis-equilibrium in the society.
Equilibrium is the law of nature, and hence disequilibrium cannot continue for long. Revolution will reestablish the equilibrium.
As capitalism will advance, its exploitation will keep on increasing. More number of people will be facing the exploitation. These situations will convert class in itself into class for itself.
C] Cycles in Capitalism
Capitalism will always face the cycle of boom and burst. Why cycle? As capitalism will advance, a greater number of people will become jobless. There will be lot of goods, but people will not be having the purchasing power. It will result into the slowdown of economy. There will be more job losses. Hence capitalism creates the conditions for its own destruction. Capitalist dig their own graves.
D] Surplus Value
Surplus values is profit. According to Marx, labour is a source of value in any good. In capitalism, capitalist does not give share to the worker in profits. Ideally worker should have share in the surplus. The surplus becomes capital. It increases the bargaining power of the capitalist. More worker works, more surplus he generates, more surplus is generated the bargaining power of capitalist increases and that of worker decreases. Hence worker is forced to work where the labour of his body is working against him.
E] Alienation
(alienation – estrangement, feeling of being separate)
From his book ‘Economic and Philosophic Manuscript.’ Inspired by Hegel and Feuerbach.
Marx wanted to show that the so-called freedom in the capitalist countries is actually alienation rather than freedom. Freedom in capitalist societies is false consciousness. Freedom means doing what one wants to do. Freedom is the source of happiness, wellbeing. For Marx real freedom is freedom from necessities. It means when the basic needs of man are fulfilled only then man is free.
Freedom can never come in capitalist society. Freedom is possible only in communism. When man is fully assured that he can do what he wants to do and society exists for protection of his basic necessities. The so-called freedom is isolation. Capitalism destroys the organic link between man and his society. It gives rise to atomistic man, the abstract individual.
It was Hegel who first explained the alienation. According to Hegel, on this earth man gets alienated from God, which is a cause of unhappiness of man. The alienation of man ends in the state because state is march of God on earth.
Feuerbach was in the group of Young Hegelians who were trying to understand Hegel. Feuerbach came to the opposite conclusion. He held that God is source of alienation. Hence to be happy, we should be free from religion. He held that God is a source of unhappiness. Why? When we look at the God, we feel bad about ourselves. God reminds us about our weakness.
Marx believed that it is not enough to be free from God, for the real freedom we need to change the basic structure of the society. How capitalism alienates man?
Capitalism does not allow man to live as per his true nature.
Man is creative by nature, man is social by nature. Capitalism destroys the human essence. In capitalism man faces alienation at four levels.
- Alienation from the process of production – the process of production has become so mechanized that man is reduced to mere cog in the wheel.
- Alienation from the product of his labour – production has become so much specialized that one does not even know, what final shape his labour has got?
- Alienation from society – working conditions are such that man does not have the scope for realization of his social nature.
- Alienation from himself – the cumulative effect of the alienation at three levels is man gets alienated from himself. Hence there is no real freedom or happiness in capitalism.
Alienation can be ended by establishing communism. By destroying capitalism. In communism man will produce what he wants. In communism there is no contradiction between man and his society.
If capitalists dig their own graves and capitalism die its own death, is there any role of human action?
“Man also makes history but only in given circumstances and not under the chosen circumstances.”
Though history is governed by law of dialectics, as per the law of dialectics, negativity get negated. Since capitalism is full of contradiction, it will automatically get negated. But it does not mean that there is no importance of human action. Hence, he inspires workers not to wait rather go for action. He says that, Man also makes history but man does not make history in chosen circumstances, he makes history only in given circumstances.
F] Concept of Freedom
Sometimes it is suggested that the terms freedom and liberty are different. However, there is no difference in freedom and liberty. Scholars use these terms interchangeably e.g. J.S. Mill gave the theory of liberty and freedom of speech and expression. Only few thinkers like Karl Marx, Hannah Arendt make difference.
Marx purposefully preferred freedom because liberty term got linked with liberalism. For Marx, so called liberty in capitalist society is false consciousness / alienation.
True freedom will come only in communism. In communism, people will work according to their ability and will get according to their need. Freedom means doing what one wants to do. This is possible only when basic necessities are fulfilled.
9] Test Your Knowledge
1] Why did Marx call his theory as Praxis?
a) It is action-based
b) It is explanation based
c) It is philosophy based
d) It is conservative in nature
Show Answer
Ans: a) It is action-based
2] Which of the following statements about Socialism is FALSE?
a) Socialism is a modern philosophy
b) It emerged as a reaction against capitalism
c) It believes in individual ownership, common use of property
d) It is based on the realization of inhumane nature of capitalism
Show Answer
Ans: c) It believes in individual ownership, common use of property
3] According to Marx, the socialism that existed before him was
a) Fabian
b) Utopian
c) Scientific
d) Market socialism
Show Answer
Ans: b) Utopian
4] Marx’s idea of anarchism is similar to that of?
a) Gandhi
b) Hobbes
c) Both Gandhi and Hobbes
d) Neither Gandhi nor Hobbes
Show Answer
Ans: a) Gandhi
5] Who made the statement, “Real is rational. Rational is real.”
a) Gandhi
b) Hegel
c) Hobbes
d) Plato
Show Answer
Ans: b) Hegel
6] Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding Dialectics?
a) It was given by Socrates
b) It represents rational debate
c) It can be represented by the equation Thesis + Antithesis = Synthesis
d) Marx rejected dialectical method
Show Answer
Ans: d) Marx rejected dialectical method
7] Which of the following statements is correct?
a) Hegel considered history as dialectical movement of idea
b) Marx considered idea as false consciousness
c) Marx gave economic interpretation of history
d) All of the above
Show Answer
Ans: d) All of the above
8] In Marx’s view, why do people form society?
a) For the task of production
b) For protection from other tribes
c) To foster culture and education
d) As a source of identity
Show Answer
Ans: a) For the task of production
9] What does Marx’s concept of ‘class for itself’ represent?
a) Low level of consciousness among workers
b) High level of consciousness among workers
c) A phase in proletarian revolution
d) The revolutionary group that will bring revolution
Show Answer
Ans: b) Higher level of consciousness among workers
10] Which of the following statements is not correct in light of Marxism?
a) Matter (not idea) is reality
b) Superstructure is independent of base
c) Manual labour is more important than intellectual labour
d) Capitalist system has two classes—haves and have nots
Show Answer
Ans: b) Superstructure is independent of base
11] Who has given ‘Law of overdetermination’?
a) Max Weber
b) Althusser
c) Gramsci
d) Karl Popper
Show Answer
Ans: b) Althusser
12] Historicism refers to
a) Scientific explanation of history
b) Politically motivated explanation of history
c) Explanation of history based on a single cause
d) Adopting multi-structural approach in studying history
Show Answer
Ans: b) Politically motivated explanation of history
13] Which of the following statements correctly explain determinism?
a) Determinism represent fundamentalism
b) It refers to scientific and multi-dimensional approach
c) It is called as non-scientific thinking
d) Both a and c
Show Answer
Ans: d) Both a and c
14] Who is the author of the book ‘Open societies and it’s enemies’?
a) Gramsci
b) Althusser
c) Karl Popper
d) Karl Marx
Show Answer
Ans: c) Karl Popper
15] Who has written the book ‘What is to be done’?
a) Lenin
b) Stalin
c) Mao Zedong
d) Gramsci
Show Answer
Ans: a) Lenin
16] Which of the following changes in Marx’s theory was not made by Lenin?
a) Revolution in feudal country
b) Incorporation of peasantry within the revolutionary class
c) Establishment of the Communist Party
d) Revolution by peaceful means
Show Answer
Ans: d) Revolution by peaceful means















In the topic : marx on false consciousness
It was Eric Hobsbawn who given concept of ” invented traditions ” in nationalism . ( Not Benedict Anderson)
Upsc interview video dekh raha tha or ek aspirant ne recommend Kiya yeh page
Do these notes available in marathi language?
There is an option in corner to change these notes in ur preferred language whatever language u know….
Correction- Its not Benedict Anderson who has given the concept of ‘uneven development’.Its Eric Hobswam
Hello ..kya koi bta skta h ki..ye notes pdne k baad subhra ma’am k notes pdne jruri h.?
no need to study shubra notes. Dont buy her notes
These are made from her notes plus some extra
They are also arranged well
Actually you can see our latest articles on our home page.. http://politicsforindia.com/ And certainly we’ll try to add more.
Thank you so much Sir.
Can’t thank enough
Well done thank a lot???
Thanks a lot Sir.Especially for the Translation from English to our mother tongue (Kannada).So that I can Understand It more better ????.By the way which application you have used to translate the text?
Thanks, Karthik. It’s just a google translator feature we’ve embedded for the purpose.
Ohk ?